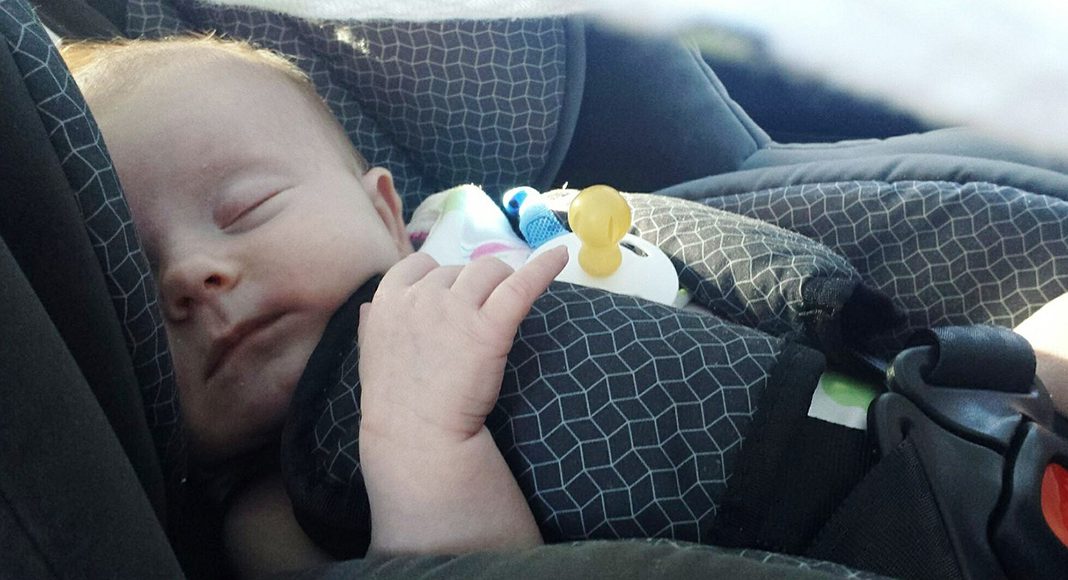
New research has revealed that newborn infants may be at risk of breathing difficulties if left in car safety seats for long periods, particularly when travelling.
Funded by the Lullaby Trust, the study was carried out at the Great Western Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust, with support from the University of Southampton and the University of Bristol.
The researchers developed a motion simulator to reproduce vertical vibration, similar to that at the base of a car safety seat in a rear-facing position in the back of a small family car. The simulator was created by the Human Factors Research Unit at the University of Southampton’s Institute of Sound and Vibration Research.
The simulator reproduced the vertical vibrations from travelling at 30mph on a straight urban road, without braking, acceleration or going over bumps.
The test allowed the team to look at how the vibrations affected babies’ heart and lung functions. They discovered that both full-term and pre-term babies showed significant signs of potentially negative cardiorespiratory effects.
Professor Peter Fleming, from the University of Bristol’s School of Social and Community Medicine, said: “This was a unique pilot study – the first to look at the physiological effect of vibration on infants in a car safety seat. The standard static car seat challenge currently used in hospitals does not reflect the angle infants are placed at, or the motion of the journey.
“Placing an infant at the more upright 40° position, along with the vibration experienced in a car, leads to significantly increased heart and respiratory rates, and decreased oxygen saturation. Simulating motion reveals a striking increase in potentially clinically significant oxygen desaturations. Surprisingly, we found these differences were similar in term and preterm infants.”
Dr Renu Arya, Consultant Paediatrician, Great Western Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust, who led the research project added: “Parents should not stop using car safety seats to transport their infants. Infants must be protected in moving vehicles, and UK law requires car seats be used whenever infants travel in cars. However, our findings support the AAP (American Academy of Paediatrics’) guideline that infant car seats should not be used as a routine infant sleep environment.”
Francine Bates, chief executive of the Lullaby Trust, advised parents to keep a watchful eye on babies travelling in a car seat: “We recommend that parents also avoid driving long distances without a break. However, avoiding the risk of injury due to a road traffic accident is paramount and fitted car seats should always be used to transport babies and toddlers. It is clear that further research is needed to explore what more we can do to ensure babies are safe and comfortable when travelling in a car seat and we will be convening an urgent summit of leading child car seat manufacturers to take this forward in the autumn.”
Click to view the full research paper: ‘Is the infant car seat challenge useful? A pilot study in a simulated moving vehicle’ by Renu Arya, Georgina Williams, Anna Kilonback, Martin Toward, Michael Griffin, Peter S Blair and Peter Fleming in Archives of Disease in Childhood.